BMS Battery Management System also called lithium-ion battery protection board, is needed in the lithium-ion battery pack. While DIY your own battery pack, you may be confused about how to choose the suitable BMS. For example, shall I need the BMS with a common port or a separate port? In this article, we will share some tips.
Step 1: Measure the resistance of the single cell and perform resistance matching
Purpose: To obtain the consistency of the individual resistances in the battery pack and improve the consistency of the battery pack’s charging and discharging efficiency.
Note: The internal resistance difference between single cells in the same group should be controlled within 0.1mΩ for A class, and within 0.5mΩ for B class. Above 1mΩ, the consistency of the battery pack will quickly deteriorate and affect the lifespan.
Step 2: Capacity classification and testing of single battery cells
Purpose: Select and pair cells with the same capacitance and voltage of the individual cells to ensure that the battery pack can effectively perform its function.
Notes:
1: The upper and lower error of capacitance in the same group does not exceed 1%, the voltage does not exceed 30mV and the charge and discharge curves are consistent (increase and voltage reduction are consistent), to fully exert the power efficiency. If the capacity difference is too large, it is easy to lose power: power outages and reduced battery pack life.
2: If there is no battery capacity analyzer to test the cell capacity, the cells must be purchased from the same brand and production batch to avoid excessive differences in capacity and voltage consistency.
Step 3: Combine battery cells and protective board(BMS)
Purpose: Complete the battery combination and cell protection circuit.
Notes:
1: Connect single cells in parallel or series to obtain the capacity and voltage of the required battery pack. Within 4 parallels, it is advisable to operate in parallel first and then in series to achieve the highest efficiency of voltage balance between cells.
2: The connecting piece (wire) material for parallel and series connection between cells is preferably red copper or red copper, followed by brass and nickel plate. It is not suitable to use metal conductors with too high resistance to connect to avoid increasing the resistance. value.
3: The wire diameter and current of the battery and protection board need to be sufficient. Try to choose a larger wire diameter to ensure the safety of the line and prevent the line temperature from producing abnormally high temperatures due to large currents. It is recommended to use 16m² of silicone wire when the design output power is below 1000W (inclusive). When the design output power is 1000W-3000W, use 35m² of silicone wire.
4: The battery core and the protection board circuit must be connected in order to avoid short circuits.
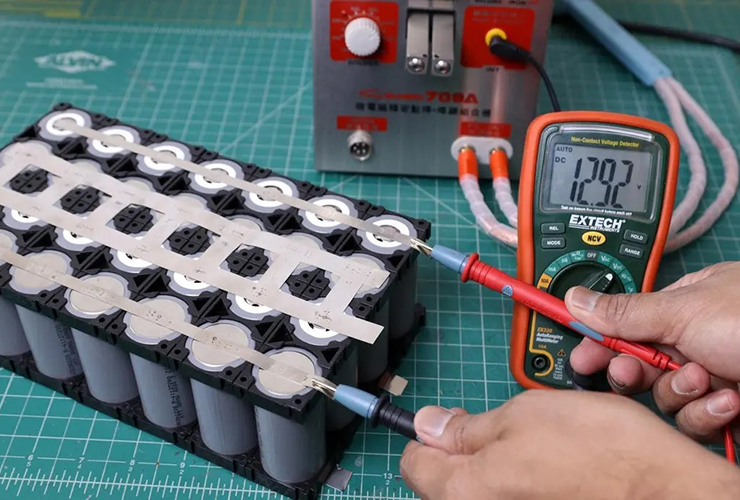
Step 4: Test the voltage of each battery cell group and check whether the BMS output is correct
Purpose: Confirm that the circuit connection method in the previous step is correct and ensure that the lithium battery protection board functions normally.
Note: For details on the detection method, please refer to the article

Step 5: Configure various components, loads, charging and discharging circuits, and switches.
Purpose: Lines, switches and insurance must be set according to the designed power and reasonably laid out.
Note: Power design must pay attention to the specifications of circuit control and components, wire diameter and insurance. At the same time, a battery main switch must be installed for safety.
Step 6: Charging Test
Purpose: Confirm that the charging function is normal.
Notes:
1: The best charging method for iron lithium batteries is CC-CV. First charge to the standard charging voltage of 14.6V with constant current (according to charger specification A), and maintain the voltage of 14.6V for about 30-60 minutes. Continue charging with a small current until the current is less than 300mA.
2: The charger must use a special charger for iron-lithium batteries. Do not use chargers for other lead-acid, ternary lithium or nickel-metal hydride batteries. Because the charging control voltage is different, there will be problems of undercharging, overcharging, and overvoltage. or dangerous.
Step 7: Loading (discharge) test
Purpose: To confirm the effectiveness of the designed output power and the normal functions of various safety insurances.
Notes:
1: Test continuously for at least 20 minutes at the maximum designed output power (or the power consumption of electrical appliances with similar loads). All wire diameters, batteries and various component configurations have no abnormal temperature rise and the safety device has no abnormal operation.
2: Each designed socket output is tested continuously for at least 20 minutes with corresponding power load. There is no abnormal temperature rise relative to the wire diameter and component configuration and there is no abnormal operation of the safety device.
Step 8: Battery Pack Packaging
Purpose: To protect the safety of the battery pack and prevent accidents
Notes:
1: The battery pack should be placed away from high temperatures, humidity, and flammable environments. The box must be insulated, moisture-resistant prevent sliding and collision, and avoid using boxes of inappropriate sizes.
2: The battery core must be firmly fixed in the box and cannot be shaken or loosened to avoid loosening of the circuit and causing a short circuit.
Skya Power designs & produces BMS for electric bicycle battery packs. Contact us for custom or production.